What is the birth control patch?
The birth control patch is a type of hormonal birth control that you wear on your skin. It looks like a thin, light brown bandage.
The sticky part of the patch has two hormones (estrogen and progestin) that are like a woman’s natural hormones. These hormones are absorbed continuously through the skin into the blood. They stop the ovaries from releasing an egg. If you don’t release an egg, you can’t get pregnant.
How well does the birth control patch work?
- There’s about an 85% chance of getting pregnant after one year of having unprotected sex.
- With typical use (this means not following the exact directions, for example you might be late changing your patch) the patch is
91% effective.
- With perfect use (this means you follow the exact directions all the time) the patch is
99.7% effective.
- There might be a higher risk of getting pregnant if you weigh more than 90 kg (198 lbs.).
- Most pregnancies happen because women forget to change their patches as directed.
- The patch doesn’t protect you from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV.
- Use a condom
every time you have sex (vaginal, oral, anal) to lower your risk of STIs and HIV.
How do I start using the patch?
To start the patch, you will need to see your health care provider. You need a prescription for the patch.
There are different ways to start the patch:
- If you start on day 1 of your period, it works right away to prevent pregnancy.
- If you start on any other day, you need to use an extra form of birth control (e.g., condoms, abstinence) for 7 days.
How do I use the patch?
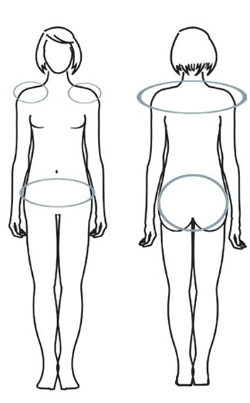
Put the patch on clean, dry skin on your upper buttocks, upper outer arm, abdomen, or upper body. Put each new patch in a different place (e.g., change between right and left sides) to keep your skin from getting irritated.
Press down firmly on the patch with the palm of your hand for 10 seconds to make sure the edges stick well.
If your skin gets irritated, take the patch off and put a new one on in another place (your patch change day stays the same).
Only use one patch at a time and:
- leave the patch on during activities (e.g., exercise, shower, swim)
- if a patch isn’t sticking, try to put it on again in a different place. If it won’t stick, take it off and put a new patch on right away. If you need a replacement patch, talk to your pharmacist or health care provider.
- be aware that used patches still contain hormones. After removing a patch, fold it inwards so it sticks to itself and put it in a garbage that is out of a child’s or pet’s reach.
- check that your patch is secure every day
- store your patches at room temperature (never put them in your fridge or freezer)
When you use the patch,
don’t:
- use any bath oil, body wash, lotion, or powder on the area where you will put your new patch
- put the patch on your breasts
- put the patch on skin that is red, cut, or scratched
- use bandages or tape to hold the patch in place as this affects how the hormones are absorbed
When do I change the birth control patch?
Your patch change day is the day of the week that you put your patch on. Always use a new patch on the same day of the week, at the same time.
You wear a patch for 1 week at a time. A new patch is put on each week for a 3-week cycle. You don’t put a patch on during week 4 (hormone-free days). This is when you get your period.
Start your next cycle by putting on a new patch after the hormone-free days. Put on a new patch, even if you still have your period. Your period should stop in a few days. If you haven’t had your period, put the patch on and call your health care provider.
Never have the patch off for more than 7 days in a row.
What are the benefits of the birth control patch?
- Your period may be more regular, lighter, and/or shorter with less cramping.
- The patch may lower your risk of getting ovarian and endometrial cancer.
- The patch may help with acne and painful periods (dysmenorrhea).
- It’s safe to use the patch for many years. There’s no need to take a break from using it.
- You can get pregnant as soon as you stop using the patch.
What are the side effects of the patch?
There is a chance (more likely in the first 3 months) that you might have:
- headaches
- tender breasts
- moodiness
- irritated skin
- slight weight gain or loss
- spotting or bleeding between periods
- Upset stomach (nausea)
- bloating (from fluid retention)
If you have side effects, don’t stop using the patch. Talk to your health care provider. Most side effects get better after 3 months.
Can the birth control patch cause blood clots?
When using the patch, there’s a small risk of blood clots in the legs, lungs, heart and/or head. The risk is higher depending on your:
- Age
- Weight (if you’re obese)
- History (or family history) of blood clots, heart attack, or stroke
- History of smoking (especially people older than 35 who smoke)
- History of migraines with aura or other nervous system problems affecting speech, vision, movement, or sensations
- Risk factors for heart disease (e.g. high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol)
- History of other medical problems (ask your health care provider about this.
The risk of getting a blood clot with the patch may be higher than with the birth control pill. The risk of getting a blood clot is higher during pregnancy and right after having a baby than when using the patch.
If you get a fever or are exposed to heat (e.g. sauna, hot tub) with the patch on, you may get more estrogen. This may increase your risk of getting a blood clot.
What symptoms do I need to watch for?
Go to the nearest emergency room or call 911 if you have:
- trouble breathing
- a very bad headache
- numbness in your arms or legs (often only on one side of the body)
- very bad pain in your abdomen, chest, or legs
- eye problems (e.g., sudden blurry vision or loss of vision)
- sudden problems with walking or balance
- sudden confusion or trouble understanding what people say to you
What if I forget to put on or change the patch?
If you forgot to put on or change your patch and it’s
less than 24 hours:
- If your patch has fallen off, try to put on the same patch. If you can’t, put on a new one right away.
- If you are late putting on the patch, put it on right away. Your patch change day stays the same. You are still protected from pregnancy.
If You Forget to Put On or Change Your Patch (for over 24 hours)
|
First Week of Use
|
Second or Third Week of Use
|
|
Patch off or late for over 24 hours (or you don’t know how long) |
Patch off for 24 to 72 hours |
Patch off for over 72 hours |
- Put on a new patch right away. This cycle will have 3 patches.
- Your patch change day stays the same.
- Use an extra form of birth control (e.g., condoms) for 7 days.
- If you have had unprotected sex in the last 5 days or the extra form of birth control fails (e.g., condom breaks), think about getting
emergency contraception to help prevent pregnancy
|
- Put on a new patch right away. Finish this cycle of patches and then start a new cycle of 3 patches. Don’t take the hormone-free break.
- Your patch change day stays the same.
- You might have spotting or miss your period this month.
Don’t take off your patch.
- You are still protected from pregnancy.
|
- Put on a new patch right away. Finish this cycle of patches and then start a new cycle of 3 patches.
Don’t take the hormone-free break.
- Your patch change day stays the same.
- You might have spotting or miss your period this month.
Don’t take off your patch.
- Use an extra form of birth control (e.g., condoms) for 7 days.
- If you have had unprotected sex in the last 5 days, or the extra form of birth control fails (e.g., condom breaks), think about getting
emergency contraception to help prevent pregnancy.
|
Did You Know
- You have the right to make the decision to have sex or not.
- Plan ahead and decide to protect yourself to lower your risk of pregnancy, STIs, and HIV.
- Many sexual health clinics offer some types of birth control for no cost for people who qualify.
- Talk to your health care provider to see if the patch is right for you (e.g. just had a baby, breastfeeding, medical problem).
- It is important to talk with your partner about how you can protect each other.
- You can get pregnant as soon as you stop using the patch.
- If you need a replacement patch, talk to your pharmacist or health clinic.
- It is safe to use the patch for many years. There is no need to “take a break” from the patch.
- Some medicines can affect the patch. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you take any medicine (prescriptions or over-the-counter).
- Don’t use the patch if you are pregnant or think you might be.
For More Information
- Health Link – Health Advice 24/7: 811